You can effectively whiten genetically discolored teeth through an all-encompassing approach combining professional treatments and at-home care. Start by consulting a dental professional to identify your specific genetic condition and develop a personalized treatment plan. Use custom-fitted trays with professional-grade whitening gel, maintain strict oral hygiene, and avoid staining foods and beverages. For stubborn cases, consider advanced options like dental bonding or veneers. Our complete guide offers deeper insights into maximizing your whitening success.
Key Takeaways
- Consult a dental professional for personalized treatment plans that account for your specific genetic condition and discoloration severity.
- Combine professional in-office whitening with custom-fitted trays for at-home maintenance using 10% carbamide peroxide gel.
- Use desensitizing products and fluoride toothpaste daily to protect genetically compromised enamel during whitening treatments.
- Consider dental bonding or porcelain veneers for severe genetic discoloration that doesn’t respond to traditional whitening methods.
- Maintain results through consistent oral hygiene, professional cleanings, and avoiding stain-causing foods and beverages.
Understanding Your Genetic Tooth Condition
While many people assume tooth discoloration simply comes from external staining, your genes play a significant role in determining both your natural tooth color and your susceptibility to certain dental conditions.
Two main genetic inheritance patterns can affect your tooth color and structure. If you have dentinogenesis imperfecta (DGI), you’ll notice blue-gray or yellow-brown discoloration caused by mutations in the DSPP gene, affecting both baby and permanent teeth. Consulting with a dental professional for guidance is crucial for developing an effective treatment strategy.
Genetic factors like DGI can permanently alter tooth color, with DSPP gene mutations causing distinctive blue-gray or yellow-brown discoloration.
Alternatively, amelogenesis imperfecta creates yellow-brown teeth with soft, prone-to-damage enamel. The condition makes teeth weak and brittle, requiring special care and treatment approaches.
Understanding your specific condition is essential because genetic tooth discoloration differs from surface stains. While external stains from coffee or wine can often be whitened, genetic conditions affect your teeth’s internal structure, making traditional whitening methods less effective.
This knowledge helps set realistic expectations for treatment options.
Professional Treatment Options That Work
When genetic tooth discoloration affects your smile, professional treatments offer powerful solutions that can’t be matched by over-the-counter products. Your dentist will create a personalized treatment plan based on your genetic profile and the severity of your discoloration. Understanding your inherited dental traits helps determine which professional whitening approach will be most effective. Patients with conditions like Amelogenesis Imperfecta require specialized care.
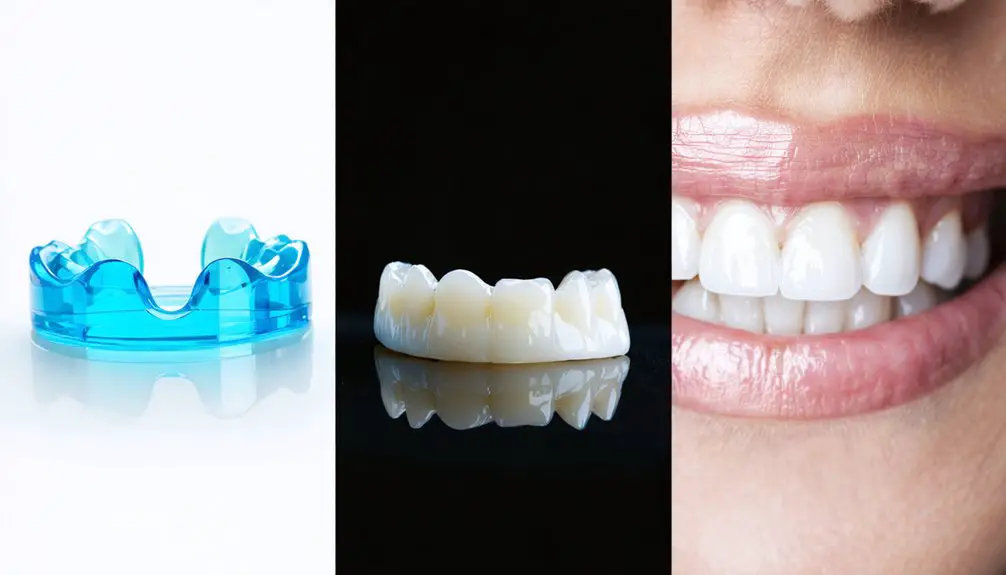
In-office whitening delivers immediate results using concentrated peroxide agents, while customized trays allow for controlled, at-home treatment with professional-grade solutions.
- Professional whitening treatments penetrate deeper into teeth, making them especially effective for genetically yellowed teeth
- Custom-fitted trays guarantee ideal contact between whitening agents and tooth surfaces
- Dental bonding can mask isolated teeth with stubborn intrinsic stains
- Porcelain veneers provide a permanent solution for widespread genetic discoloration when whitening isn’t enough
At-Home Care Strategies for Better Results
Although professional treatments provide powerful whitening solutions, you can achieve significant improvements through carefully planned at-home care strategies.
Start with custom-fitted trays and 10% carbamide peroxide gel for best results, wearing them overnight to guarantee consistent contact. While exploring home remedies, combine baking soda with hydrogen peroxide no more than twice weekly to prevent enamel damage. Consult a dentist before beginning any whitening regimen to ensure your teeth and gums are healthy enough for treatment.
Focus on enamel protection by using fluoride toothpaste daily and incorporating desensitizing products containing potassium nitrate. The whitening toothpaste abrasives can help reduce surface stains over time.
You’ll need patience, as results develop gradually over several weeks. Maintain your progress by avoiding stain-causing foods and beverages while practicing thorough oral hygiene.
If you experience sensitivity, rinse thoroughly after treatments and temporarily avoid extremely hot or cold items until discomfort subsides.
Combining Treatments for Maximum Impact
Since genetic and deep discoloration often require multiple approaches, combining professional treatments can dramatically enhance your whitening results. Good oral hygiene is essential for maintaining treatment effectiveness and preventing future staining. Regular dental check-ups help monitor treatment progress and adjust combinations as needed. By leveraging treatment synergy between different methods, you’ll achieve maximum aesthetic enhancement for your patients’ smiles. Professional in-office bleaching combined with take-home treatments provides an all-encompassing foundation, while additional interventions target specific concerns.
- Start with combined professional whitening and surface treatments for initial color improvement
- Consider dental bonding for localized intrinsic stains that remain after whitening
- Evaluate porcelain veneers for severe genetic discoloration when other treatments prove insufficient
- Explore internal bleaching options for root canal-treated teeth, especially when combined with external whitening
These strategic combinations allow you to address multiple aspects of discoloration, delivering more predictable and satisfying outcomes for your patients.
Maintaining Long-Term Whitening Success
Maintaining your whitening results requires a thorough approach that combines proper oral hygiene, dietary awareness, and strategic touch-up treatments.
To implement effective long-term strategies, brush twice daily with whitening toothpaste and use an electric toothbrush with a timer for ideal cleaning. Schedule regular dental cleanings and follow your dentist’s recommended touch-up timeline, typically every 2-3 years for professional treatments. Using high-concentration bleaching gel during professional treatments ensures optimal whitening results. Professional treatments can deliver lasting results up to three years with proper maintenance.
Understanding dietary impacts is vital for preserving your bright smile. Use straws when drinking staining beverages like coffee or wine, and rinse your mouth with water after consuming pigmented foods.
Follow a “white diet” immediately after treatments, and maintain consistent hydration to support natural cleaning mechanisms. For best results, avoid tobacco products and minimize acidic foods that can weaken your enamel and accelerate discoloration.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Genetic Tooth Discoloration Worsen With Age?
Progressively prominent genetic factors can make your teeth’s discoloration worsen over time, as aging effects thin your enamel, expose more dentin, and increase your susceptibility to stains and erosion.
Are Whitening Treatments Covered by Dental Insurance for Genetic Conditions?
You’ll rarely find whitening options covered by insurance policies for genetic conditions, but some plans may offer partial coverage if you can prove medical necessity through documented enamel damage.
How Do Medications Interact With Professional Whitening for Genetic Tooth Discoloration?
You’ll need to discuss your medications with your dentist, as they can affect whitening safety and outcomes. Some drugs require timing adjustments or alternative treatments to guarantee ideal results for genetic discoloration.
Do Siblings Always Inherit the Same Type of Tooth Discoloration?
You’ll find inheritance patterns vary considerably among siblings – they don’t always share identical tooth discoloration. Different gene expressions and environmental factors create unique sibling comparisons, even within the same family.
Can Genetic Tooth Discoloration Skip Generations in Families?
Yes, your family traits of tooth discoloration can skip generations, especially with autosomal recessive hereditary factors where parents carry the gene but don’t show symptoms themselves.
References
- https://www.i20familydental.com/blog/2023/10/13/all-about-teeth-whitening-and-genetics/
- https://www.airportroaddental.com/tooth-discoloration-causes-types-and-treatment
- https://www.salinasdental.com/blog/can-discolored-and-stained-teeth-be-hereditary/
- https://www.perfectsmiles.net/2024/06/17/genetics-and-discolored-teeth/
- https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/tooth-discoloration
- https://www.fsdentalarts.com/blog/?p=49
- https://www.deandentalcare.com/blog/2021/08/12/stained-teeth-genetics/
- https://www.budadental.com/blog/stained-teeth-and-the-role-of-genetics/
- https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/dentinogenesis-imperfecta/
- https://mystldentist.com/teeth-whitening-and-the-role-of-genetics-what-you-cant-control/