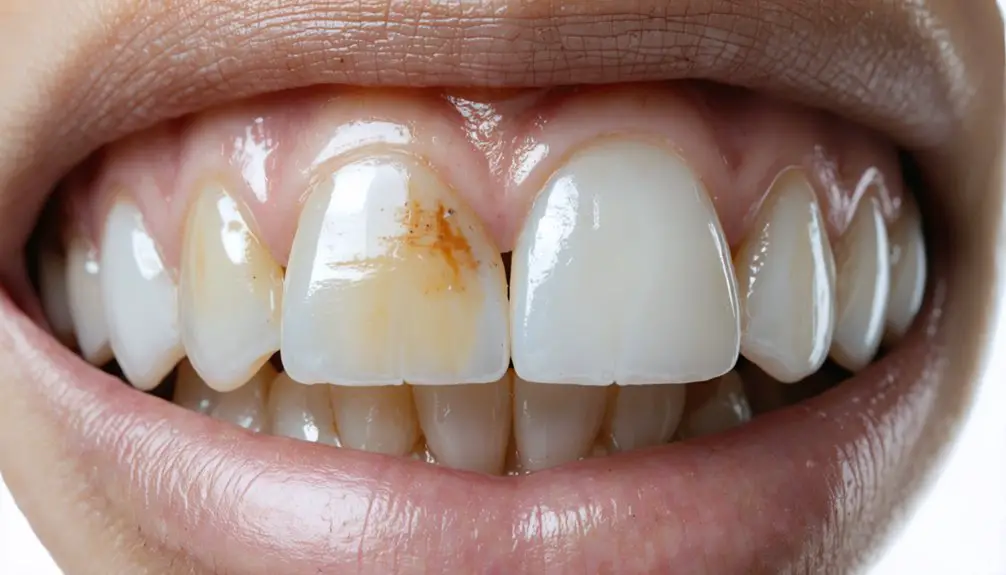
For genetic tooth discoloration, you’ll need professional evaluation to determine the most effective treatment approach. While in-office whitening using high-concentration peroxide can help with mild cases, severe genetic staining often requires advanced solutions like porcelain veneers or dental bonding. Your dentist can customize treatment based on your specific condition, combining multiple techniques for best results. Understanding your treatment options and their long-term effectiveness will help you make an informed decision about your dental care.
Key Takeaways
- Professional in-office whitening treatments using high-concentration peroxide provide quick results for mild to moderate genetic discoloration.
- Porcelain veneers offer permanent coverage of severe genetic stains while preserving natural tooth structure.
- Dental bonding provides immediate masking of genetic discoloration and can address structural imperfections simultaneously.
- Custom take-home whitening kits with professional-grade gels allow controlled treatment for genetically stained teeth.
- A combination of treatments may be necessary, as genetic discoloration often requires multiple approaches for optimal results.
Understanding Genetic Tooth Discoloration
While many people assume tooth discoloration stems purely from lifestyle factors, genetic conditions can greatly impact tooth color and structure from early development.
Two primary inherited conditions, dentinogenesis imperfecta and amelogenesis imperfecta, cause significant discoloration through mutations affecting tooth formation.
Your genetic factors determine your enamel thickness and transparency, which directly influence tooth color. If you’ve inherited thin enamel, more of the yellowish dentin underneath shows through.
Additionally, genetic mutations can disrupt normal mineralization processes, leading to intrinsic staining that occurs deep within the tooth structure.
These inherited conditions often result in grayish or yellow-brown discoloration and may cause structural vulnerabilities like weak, brittle teeth prone to chipping and decay. Poor oral hygiene can further worsen existing genetic discoloration issues.
Understanding your genetic predisposition helps determine the most effective treatment approach. Professional treatment options like dental crowns and veneers can effectively address genetic tooth discoloration.
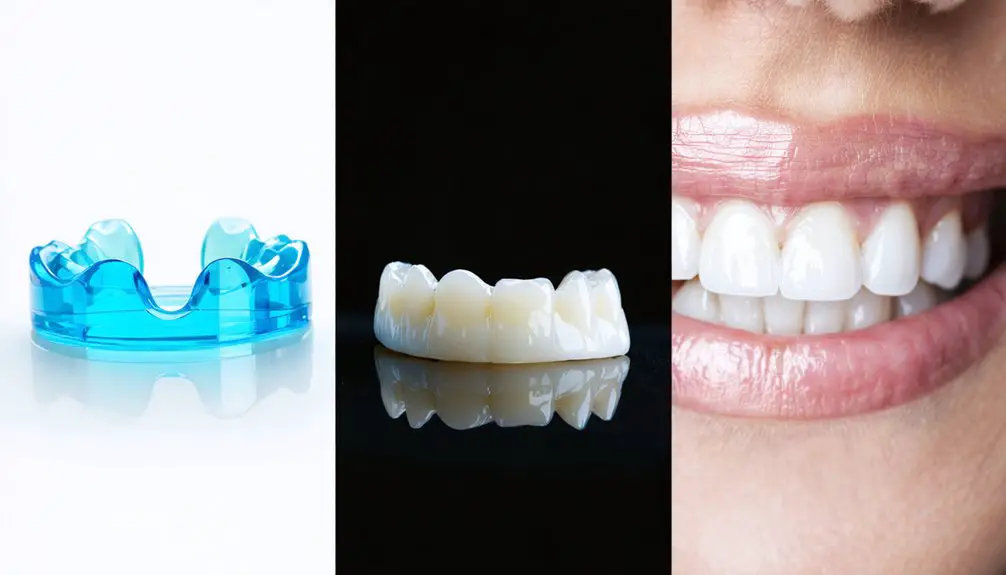
Professional Whitening Treatment Options
Although genetic tooth discoloration presents unique challenges, professional whitening treatments offer scientifically-proven solutions through both in-office procedures and take-home options.
In-office treatments utilize high-concentration hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide under professional supervision, delivering noticeable results in about an hour while minimizing sensitivity risks. The oxygen molecules released during treatment penetrate tooth layers to break down stubborn genetic stains. Understanding enamel thickness variations helps dentists customize treatment intensity for optimal results.
Custom take-home kits complement these treatments with professionally-fitted trays and specialized whitening gels. You’ll apply these daily for 30-60 minutes over several weeks, allowing for targeted treatment of genetically-influenced discoloration.
Your dentist will assess your genetic predisposition to determine ideal treatment intensity and duration, while monitoring for sensitivity. If whitening alone proves insufficient, they may recommend additional cosmetic procedures such as dental bonding or veneers to achieve your desired results.
Advanced Solutions With Porcelain Veneers
Porcelain veneers represent a sophisticated solution for treating genetic tooth discoloration, particularly when traditional whitening methods prove insufficient.
Porcelain veneers offer an advanced approach to treating stubborn genetic tooth staining when standard whitening fails to achieve desired results.
You’ll find that these thin porcelain shells effectively mask intrinsic stains while preserving your natural tooth structure through minimal enamel reduction.
For ideal aesthetic considerations, feldspathic porcelain offers exceptional translucency that mimics natural enamel.
Your dentist can enhance veneer longevity through immediate dentin sealing and precise bonding techniques.
When severe discoloration exists, they’ll often utilize opaque composite sublayers beneath the porcelain to guarantee complete masking while maintaining a natural appearance.
You’ll benefit from veneers’ superior stain resistance compared to natural enamel, and they can simultaneously address minor shape and alignment concerns.
With proper care and maintenance, patients can expect their veneers to provide lasting aesthetic results for 10-15 years.
This conservative approach delivers predictable, lasting results for patients with genetic discoloration resistant to conventional whitening methods.
Unlike temporary whitening treatments that require frequent touch-ups, veneers provide permanent coverage of deep stains.
Dental Bonding as an Alternative Approach
If you’re seeking an alternative to traditional whitening for genetically discolored teeth, dental bonding offers distinct advantages through its ability to completely mask discoloration using composite resin material that’s color-matched to your desired shade.
The application process involves preparing the tooth surface, applying the composite resin in precise layers, and then shaping and polishing it to achieve natural-looking results that can last several years. Dentist-approved treatments are recommended to maintain and brighten composite bonding when needed. Unlike natural teeth, composite resin is resistant to whitening agents.
You’ll need to maintain your bonded teeth through regular dental cleanings and possible touch-ups every 3-5 years, as the composite material can become stained from common substances like coffee or wine.
Benefits Over Traditional Whitening
While traditional teeth whitening effectively addresses external stains, dental bonding offers superior benefits for patients with genetic discoloration.
The bonding advantages include immediate concealment of intrinsic stains and the ability to customize both color and shape in a single procedure. You’ll achieve predictable, uniform results through aesthetic customization, regardless of the underlying genetic condition. The composite resin is carefully matched to natural teeth for seamless results. One visit completion makes bonding highly convenient for busy patients.
Unlike whitening treatments that may require multiple sessions with varying outcomes, bonding delivers instant transformation by covering discolored areas with composite resin.
You can address chips, gaps, and structural imperfections simultaneously while masking discoloration. Though bonding costs more initially, it provides extensive smile enhancement that whitening alone can’t achieve.
The non-porous materials resist staining better than natural teeth, and with proper maintenance, you’ll maintain lasting results that effectively conceal genetic discoloration.
Application Process and Results
The application of dental bonding involves four key phases to effectively mask genetic discoloration.
First, you’ll undergo teeth whitening followed by a two-week stabilization period to guarantee ideal surface adhesion.
Then, your dentist will select a composite resin that matches your newly whitened teeth through precise color matching techniques.
During the procedure, your dentist will apply the tooth-colored resin, carefully sculpting it to achieve the desired shape before using a special curing light to harden the material.
Finally, they’ll polish the bonded surface to match your natural teeth’s luster.
While bonding techniques provide immediate results that can last several years, you should note that the composite material won’t respond to future whitening treatments.
If discoloration occurs, you’ll need professional replacement to maintain aesthetic uniformity.
Maintenance and Touch-Up Needs
Since dental bonding material doesn’t respond to traditional whitening agents, maintaining your bonded teeth requires a different approach than natural teeth.
To optimize your maintenance strategies, you’ll need to schedule regular professional cleanings and implement preventive measures against staining. While composite bonding resists stains better than natural enamel, it can still discolor over time.
For touch-up techniques, your dentist can repair or replace discolored bonding material to match adjacent teeth. This process typically involves applying new composite resin with minimal tooth preparation.
You’ll maximize long-term results by avoiding tobacco, coffee, and red wine while using non-abrasive toothpaste and gentle brushing techniques.
If extensive discoloration occurs, your dentist may recommend alternative solutions such as veneers or crowns to restore your smile’s uniformity.
Comprehensive Care for Severe Cases
Managing severe genetic tooth discoloration requires a multi-faceted treatment approach combining professional whitening techniques with restorative options.
You’ll need to take into account both in-office bleaching with concentrated peroxide agents and internal whitening procedures for teeth with root canal treatments. For genetic conditions affecting enamel integrity, porcelain veneers or full crowns may provide ideal results.
Your dentist might recommend starting with minimally invasive techniques like microabrasion combined with professional bleaching.
If these prove insufficient, restorative solutions such as veneers, bonding, or crowns can mask stubborn intrinsic stains.
Custom-fitted take-home bleaching trays can supplement in-office treatments, offering prolonged contact time for enhanced whitening effects.
This all-encompassing strategy guarantees the most effective outcome for severe genetic discoloration cases.
Long-Term Maintenance and Results
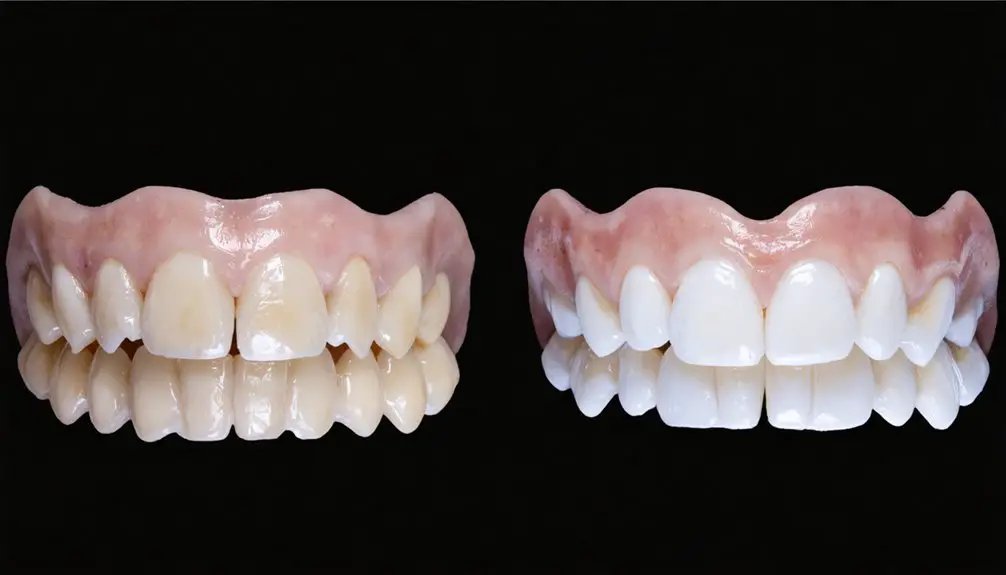
Maintaining successful whitening results for genetic tooth discoloration requires a well-structured, long-term commitment to both clinical and at-home care protocols.
You’ll need to establish consistent oral hygiene practices, including twice-daily brushing with fluoride toothpaste and daily flossing. Regular professional cleanings and periodic touch-ups of your whitening treatment will help sustain the results.
Your home care routine should incorporate whitening toothpaste several times weekly, especially after professional treatments.
Essential dietary adjustments include limiting exposure to staining substances like coffee, tea, and red wine. When you do consume these beverages, use a straw and rinse immediately with water.
For severe cases with porcelain veneers or dental bonding, you’ll need scheduled maintenance visits to monitor wear and address any recurring discoloration promptly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Genetic Tooth Discoloration Worsen With Age?
Yes, your genetic factors can intensify tooth discoloration as you age. Age effects like enamel thinning, dentin darkening, and reduced saliva production often accelerate discoloration in genetically predisposed teeth.
Are There Any Natural Remedies Effective for Genetic Tooth Staining?
Like seeking sunshine in a storm, you’ll find natural treatments and herbal solutions can’t penetrate genetic tooth staining. These remedies only address surface discoloration, not your inherited deeper tooth structure.
How Soon After Whitening Treatment Can I Eat Normally?
After whitening procedures, you’ll need to wait 24-48 hours before eating normally. Follow post-treatment care guidelines by consuming only soft, non-staining foods initially and drinking plenty of water during recovery.
Does Insurance Typically Cover Treatments for Genetic Tooth Discoloration?
Like steering through choppy waters, your insurance coverage for genetic tooth discoloration varies widely. Treatment options may be covered if deemed medically necessary, but purely cosmetic procedures typically aren’t eligible for benefits.
Can Genetic Tooth Discoloration Skip Generations in Families?
Yes, genetic tooth discoloration can skip generations when you’ve inherited traits through autosomal recessive or X-linked patterns. Your family history may show carriers without symptoms passing mutations to later generations.
References
- https://www.dentistryofthequeencity.com/2024/11/treatment-options-for-tooth-discoloration/
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/10958-tooth-discoloration
- https://www.summercreekdentistry.com/blog/2024/02/15/can-your-genes-cause-tooth-stains/
- https://www.i20familydental.com/blog/2023/10/13/all-about-teeth-whitening-and-genetics/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9712005/
- https://www.deandentalcare.com/blog/2021/08/12/stained-teeth-genetics/
- https://www.gatewayfamilydentist.com/can-genetics-cause-tooth-discoloration
- https://www.beverlyfarmsdental.com/blog/2022/06/15/can-genetics-cause-stained-teeth/
- https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/dentinogenesis-imperfecta/
- https://www.salinasdental.com/blog/can-discolored-and-stained-teeth-be-hereditary/