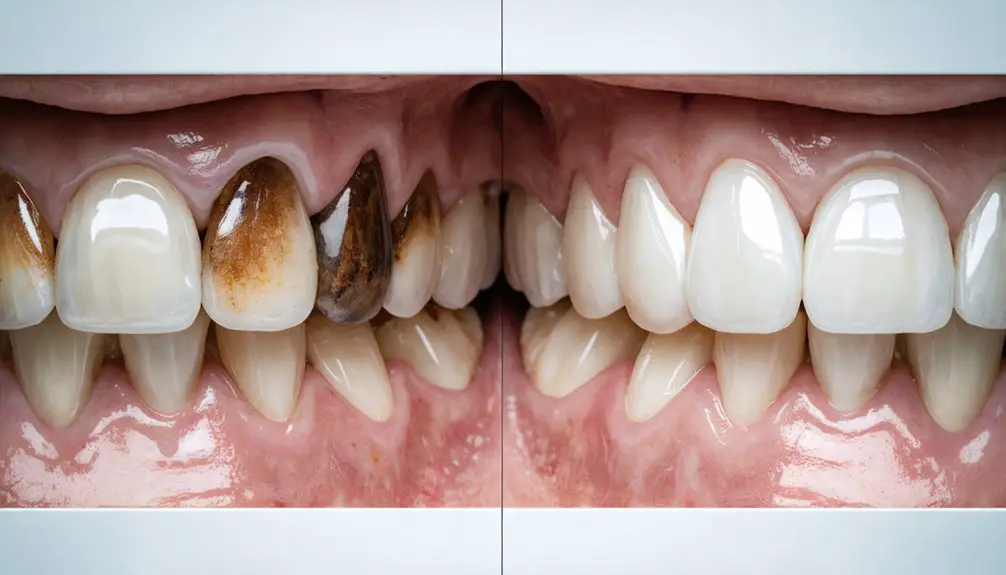
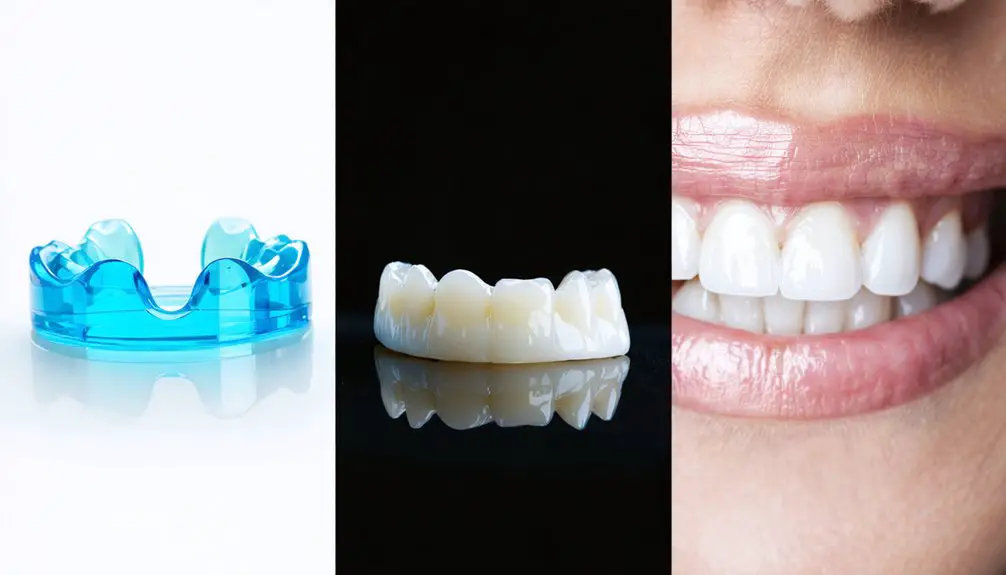
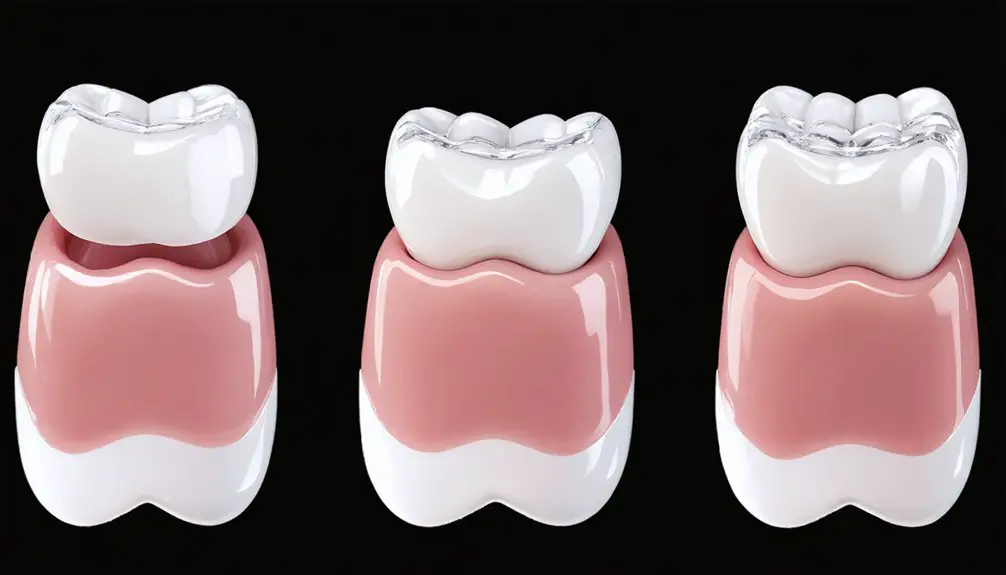
You’ll find several effective options for treating genetic tooth discoloration, from professional whitening treatments using high-concentration peroxide gels to cosmetic solutions like dental bonding and porcelain veneers. For conditions like amelogenesis imperfecta or dentinogenesis imperfecta, your dentist may recommend extensive treatments combining preventative care with restorative procedures. The severity of your discoloration and structural concerns will determine which approach can deliver ideal aesthetic and functional results.
Key Takeaways
- In-office bleaching with high-concentration peroxide gels and light activation provides deep penetration for inherited tooth stains.
- Custom-fitted take-home whitening trays with 10-20% carbamide peroxide offer flexible treatment for genetic discoloration.
- Porcelain veneers provide a long-lasting solution by covering genetically stained teeth with stain-resistant ceramic shells.
- Dental crowns completely encase affected teeth, offering both aesthetic improvement and structural support for weakened teeth.
- Composite bonding uses tooth-colored resins to mask discoloration while preserving natural tooth structure.
Understanding Genetic Tooth Discoloration and Its Causes
While many people associate tooth discoloration with lifestyle factors like coffee consumption or smoking, genetic conditions can cause intrinsic tooth staining that’s far more challenging to address.
Two primary genetic factors can greatly impact tooth structure and color: dentinogenesis imperfecta and amelogenesis imperfecta. These inherited conditions affect how your teeth develop, causing structural defects in the enamel and dentin.
Genetic dental conditions like dentinogenesis and amelogenesis imperfecta can dramatically alter tooth structure, leading to permanent developmental defects.
Dentinogenesis imperfecta results in grayish, transparent enamel and brittle teeth, while amelogenesis imperfecta produces yellow-brown discoloration with soft, fragile enamel prone to decay. Regular dental check-ups are essential for monitoring these conditions.
Even without these specific conditions, your genetic makeup influences your natural tooth color through inherited traits affecting enamel thickness and translucency. This often means that store-bought whitening products may provide limited whitening results.
Thinner enamel reveals more of the underlying yellow dentin, while thicker enamel typically appears whiter.
Professional Whitening Methods for Inherited Stains
If you’re struggling with inherited tooth discoloration, professional whitening methods offer several targeted approaches through in-office treatments and customized take-home systems.
Your dentist can provide high-concentration peroxide treatments activated by advanced technologies like laser systems, which penetrate deep into the tooth structure to address intrinsic stains.
These professional options, combined with careful monitoring and protective measures, can yield significant improvements while minimizing sensitivity and other potential side effects. A thorough dental evaluation is essential before beginning any whitening treatment to determine the exact nature of the discoloration. For optimal results, dentists may recommend combination therapies that utilize multiple treatment methods to address complex discoloration cases.
In-Office Bleaching Techniques
When addressing genetic tooth discoloration, professional in-office bleaching techniques represent the most potent approach available.
Your dentist will use high-concentration peroxide gels that penetrate deep into your enamel to chemically alter the inherited stains. Since genetic discoloration often results in intrinsic stains, specialized treatments are essential for effective removal. These in-office techniques typically involve 60-minute sessions under careful professional supervision.
To enhance the whitening process, your dentist may employ light or laser activation methods to catalyze the bleaching agents. Treatments using light activation can help accelerate the whitening process while minimizing tooth sensitivity.
For particularly challenging cases of genetic discoloration, they’ll often combine multiple approaches, including targeted internal bleaching for individual teeth or microabrasion techniques.
You’ll receive a customized treatment protocol based on your specific type of genetic staining, tooth sensitivity, and overall oral health.
These professional methods offer considerably stronger whitening action than over-the-counter alternatives.
Take-Home Tray Systems
Professional take-home tray systems offer a powerful yet controlled approach for treating genetic tooth discoloration under dental supervision.
You’ll receive custom-fitted trays precisely molded to your dental anatomy through impressions or digital scanning, ensuring ideal contact with stained surfaces while protecting soft tissues. Dentists recommend thorough tray cleaning after each use to maintain optimal hygiene and effectiveness. Our professional team provides ongoing support guidance throughout your whitening journey to ensure optimal results.
The take-home benefits include:
- Higher-strength peroxide gels (10-20% carbamide peroxide) tailored to your specific stain severity
- Flexible treatment scheduling with daily wear times from 30 minutes to several hours
- Tray customization that prevents gel leakage and reduces sensitivity risks
- Consistent monitoring by your dentist to adjust treatment protocols based on your response
Treatment typically spans 2-4 weeks, with noticeable improvements within the first week.
Your dentist will provide detailed instructions to maximize results while maintaining your oral health throughout the whitening process.
Advanced Whitening Technologies
Advanced whitening technologies represent the cutting edge of treatment options for genetic tooth discoloration, offering powerful in-office solutions that surpass conventional methods.
These professional treatments utilize high-concentration peroxide agents that penetrate deep into your tooth structure to break down inherited stains through oxidation. Professional supervision from experienced dental staff ensures safe, optimal results. Several genetic variations in the AMELX gene directly influence how teeth respond to whitening treatments.
While light-activated whitening systems like Zoom! claim to enhance results, current research doesn’t conclusively prove their superiority over peroxide alone.
However, these treatments can reduce your chair time to under an hour. Treatment safety remains paramount – your dentist will protect soft tissues and carefully monitor the process to minimize sensitivity.
For stubborn genetic stains, you may need multiple sessions or touch-ups every 5-7 years. If whitening doesn’t achieve your desired results, your dentist might recommend additional cosmetic options like veneers.
Dental Bonding as a Conservative Treatment Approach
Your dentist will begin the bonding process by preparing your tooth’s surface with a mild etching solution and applying a color-matched composite resin material.
The resin is then carefully sculpted to achieve natural contours and hardened using a specialized curing light, completing the restoration in a single visit.
To maintain your bonded teeth’s appearance, you’ll need to minimize exposure to staining agents and practice diligent oral hygiene, as the composite material can be more susceptible to discoloration than natural enamel.
Bonding Process and Materials
Dental bonding represents a conservative treatment approach for genetic tooth discoloration, utilizing composite resins and specialized adhesive systems to enhance tooth aesthetics. The process employs tooth-colored bonding materials carefully selected to match your natural shade, while preserving healthy tooth structure.
- Your dentist begins by preparing the tooth surface with a mild etching solution, creating microscopic roughness for ideal resin application and adhesion.
- Multiple layers of composite resin are strategically applied and shaped to achieve natural-looking results.
- A specialized blue LED light cures and hardens each layer of resin to guarantee durability.
- The restoration is meticulously finished and polished using multi-fluted carbide burs and polishing discs to create a seamless blend with adjacent teeth.
Managing Post-Treatment Appearance
While composite bonding offers an effective solution for genetic tooth discoloration, managing post-treatment appearance requires consistent patient commitment and proper maintenance protocols.
You’ll need to avoid staining foods and beverages for at least 48 hours after the procedure to protect the bonding’s aesthetics.
To maximize bonding longevity, which typically ranges from 4-8 years, maintain thorough oral hygiene and attend regular dental cleanings.
Be mindful of post-treatment sensitivity, which may occur due to temperature changes affecting the resin material.
You can preserve your results by avoiding habits that might chip or damage the bonding, using gentle brushing techniques, and selecting non-abrasive toothpastes.
Regular monitoring by your dentist guarantees early detection of wear or discoloration, potentially extending the life of your bonding to 5-10 years.
Porcelain Veneers: A Long-Term Solution
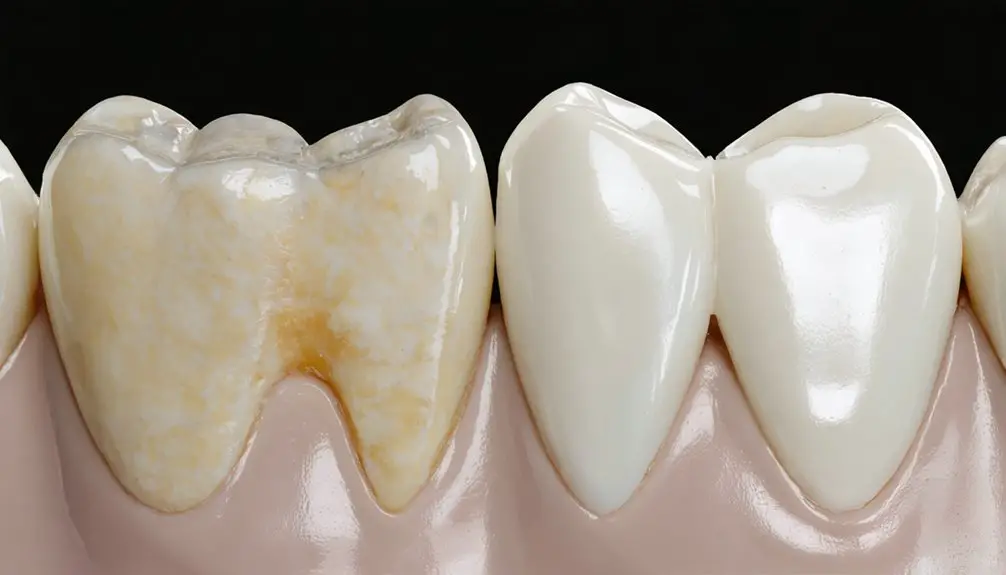
Patients seeking permanent solutions for genetic tooth discoloration often find porcelain veneers to be an ideal choice, as these custom-fabricated ceramic shells effectively conceal both intrinsic and extrinsic staining. The veneer advantages include exceptional durability and stain resistance, typically lasting 10-15 years with proper maintenance.
Porcelain veneers provide a lasting solution for tooth discoloration, offering durable, stain-resistant coverage that transforms smiles for over a decade.
- High-translucency porcelain materials mimic natural enamel’s light-reflecting properties
- Advanced bonding technology guarantees secure adhesion while preserving healthy tooth structure
- Digital scanning enables precise customization for superior fit and aesthetics
- Conservative treatment approach maintains more natural tooth structure compared to crowns
Your veneers will resist staining better than natural teeth or resin composites, maintaining their aesthetic appeal with routine dental hygiene.
This long-term solution offers both functional and cosmetic benefits, improving your smile’s appearance while protecting underlying tooth structure.
Advanced Treatments: Crowns and Internal Bleaching
For individuals with severe genetic tooth discoloration, advanced treatments like crowns and internal bleaching provide robust solutions when conventional methods prove insufficient.
Internal bleaching works effectively on root canal-treated teeth by placing whitening agents directly inside the tooth structure to lighten discoloration from within. You’ll find this particularly useful for addressing grayish or dark stains caused by genetic conditions.
Dental crowns offer a more thorough approach by fully encasing affected teeth. They’re especially beneficial when structural weakness accompanies genetic enamel defects.
While crowns require more tooth reduction, they deliver reliable, long-term aesthetic results and functional restoration. Your dentist might recommend combining both treatments – using internal bleaching first to achieve ideal shade before crown placement, maximizing the final aesthetic outcome.
Managing Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Comprehensive Strategy
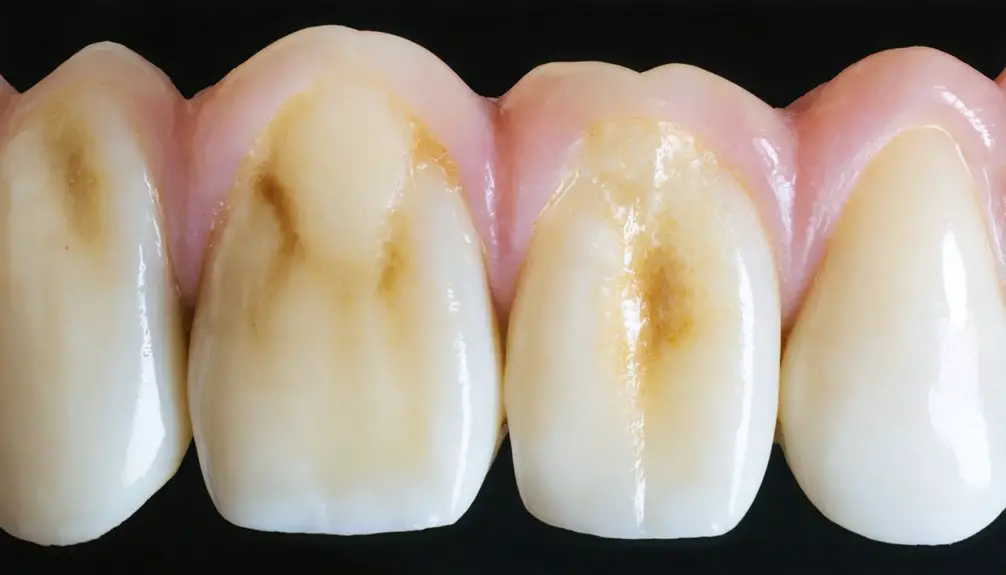
Successfully managing amelogenesis imperfecta requires a thorough, multifaceted approach that integrates preventative care, restorative treatments, and psychosocial support. A multidisciplinary approach guarantees ideal outcomes through coordinated interventions at each stage of dental development.
- Your preventative care strategy should include desensitizing toothpaste, strict oral hygiene, and regular dental monitoring to prevent complications.
- Early-phase treatment focuses on composite restorations and temporary crowns to protect teeth during developmental stages.
- Restorative options range from direct composite bonding for mild cases to more durable indirect restorations like porcelain veneers or zirconia prosthetics.
- Your treatment plan must address both functional and aesthetic concerns, incorporating orthodontic alignment when needed while considering the psychological impact on your quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Genetic Tooth Discoloration Treatments Typically Covered by Dental Insurance?
You’ll find treatment coverage for genetic tooth discoloration is quite limited, as most insurance policies classify these procedures as cosmetic unless they’re medically necessary to restore compromised tooth function.
Can Genetic Tooth Discoloration Skip Generations in Families?
Yes, your genetic tooth discoloration can skip generations due to hereditary factors like recessive inheritance, X-linked patterns, and carrier status, creating complex familial patterns that don’t follow direct parent-to-child transmission.
At What Age Should Children With Genetic Tooth Discoloration Begin Treatment?
You’ll want to start children’s dental care evaluations by age 2, with treatment timing typically beginning between ages 6-8 when permanent front teeth emerge, depending on discoloration severity and dental maturity.
Can Genetic Tooth Discoloration Worsen With Age or Pregnancy?
Like waves eroding a shoreline, your genetic tooth discoloration will intensify with aging as enamel thins naturally. Pregnancy’s hormonal changes and increased oral acidity can accelerate this deterioration through weakened enamel protection.
Are There Specific Dietary Restrictions After Treating Genetic Tooth Discoloration?
You’ll need to make dietary changes after treatment, avoiding staining substances like coffee, tea, wine, and acidic drinks for at least 48 hours to preserve treatment effects and maintain results.
References
- https://www.havertowndentalarts.com/teeth-whitening-for-intrinsic-tooth-stains/
- https://www.dentistryofthequeencity.com/2024/11/treatment-options-for-tooth-discoloration/
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/10958-tooth-discoloration
- https://www.dentalxlnc.com.au/top-4-treatments-for-tooth-discolouration-removal-of-stains/
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/amelogenesis-imperfecta
- https://www.deandentalcare.com/blog/2021/08/12/stained-teeth-genetics/
- https://www.fsdentalarts.com/blog/?p=49
- https://www.salinasdental.com/blog/can-discolored-and-stained-teeth-be-hereditary/
- https://www.beverlyfarmsdental.com/blog/2022/06/15/can-genetics-cause-stained-teeth/
- https://www.gatewayfamilydentist.com/can-genetics-cause-tooth-discoloration