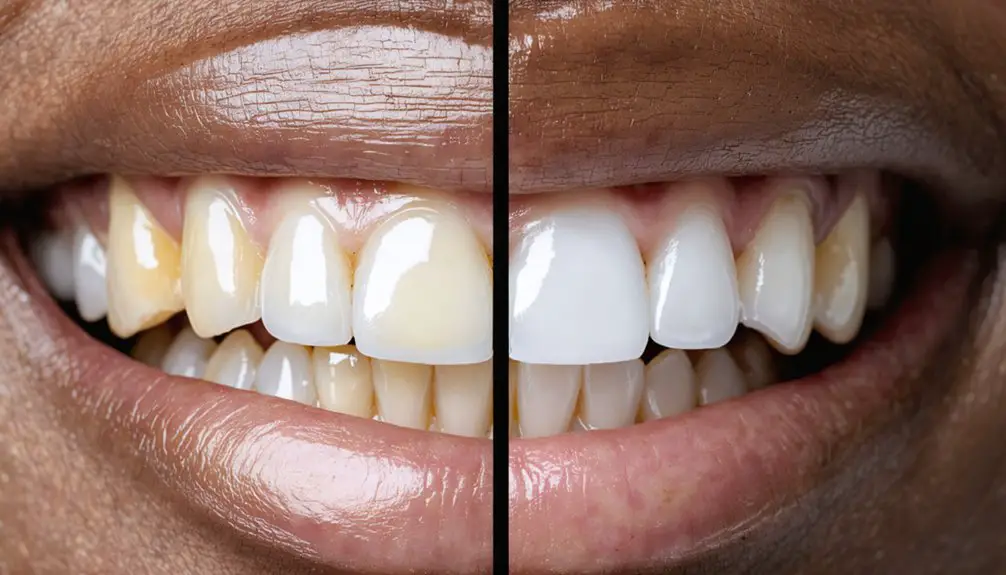
When dealing with genetic tooth discoloration, you’ll need specialized treatments beyond standard whitening. Start with a professional dental assessment to determine your specific condition and treatment plan. Consider professional options like light therapy or porcelain veneers for severe cases, and maintain results with proper oral hygiene and stain-prevention habits. Use desensitizing products, track your progress, and work closely with your dentist to manage sensitivity. Understanding your unique genetic factors will help you achieve the best possible outcome.
Key Takeaways
- Consult a dental professional for a thorough assessment to determine the specific genetic condition affecting tooth color before starting treatment.
- Choose professional whitening treatments over home kits for genetic discoloration, as they offer stronger, more controlled results under expert supervision.
- Consider combination treatments like initial whitening followed by veneers or bonding for severe genetic discoloration cases.
- Use desensitizing products before and during treatment to manage tooth sensitivity, especially if genetically predisposed.
- Track progress with regular photos and dental check-ups every 4-6 weeks to ensure treatment effectiveness and make necessary adjustments.
Understanding Your Genetic Tooth Condition
While many people assume tooth discoloration simply comes from external staining, genetic factors can play a significant role in how your teeth look and respond to whitening treatments.
Two main genetic conditions, dentinogenesis imperfecta and amelogenesis imperfecta, can cause intrinsic staining that affects your teeth’s internal structure.
If you’ve noticed your teeth have an unusual grayish, blue-gray, or yellow-brown color that doesn’t improve with regular cleaning, you may have inherited one of these conditions.
Natural genetic variations in enamel translucency and thickness can also influence your tooth color and whitening results.
Understanding your specific genetic condition is essential because intrinsic staining requires different treatment approaches than surface stains from food or drinks.
These genetic conditions often result in weak, brittle teeth that may need additional protection beyond whitening treatments.
Store-bought whitening products may prove ineffective, making professional whitening the recommended choice for genetic discoloration.
A professional dental evaluation can determine whether your discoloration stems from genetic factors.
Professional Dental Assessment First
Before pursuing any whitening treatment for genetically discolored teeth, you’ll need a thorough professional dental assessment. Your dentist will conduct extensive diagnostic imaging and may recommend genetic counseling to understand your specific condition.
Your professional assessment will include:
A comprehensive dental assessment is essential for understanding your genetic tooth discoloration and developing an appropriate treatment strategy.
- Visual examination of your teeth’s color, texture, and enamel integrity to identify genetic abnormalities.
- X-rays or CT scans to detect structural changes invisible to the naked eye.
- Review of your family dental history to establish inheritance patterns.
- Functional testing to evaluate tooth sensitivity and strength.
This evaluation helps determine if your discoloration stems from genetic factors like amelogenesis imperfecta or dentinogenesis imperfecta. If genetic testing reveals variations in the DSPP gene, your treatment options may be limited. The examination will also reveal if you have intrinsic staining, which requires different treatment approaches than external discoloration.
With these insights, your dental team can develop a safe, effective treatment plan that protects your teeth while addressing aesthetic concerns.
Choosing the Right Whitening Treatment
When choosing between professional whitening and at-home options for genetic tooth discoloration, you’ll need to take into account that professional treatments offer more potent, controlled results while home treatments work best for mild cases.
Your safety and oral health should guide your treatment selection, as genetic discoloration often requires specialized approaches beyond standard whitening methods. Special light therapy during in-office treatments can enhance the whitening process for stubborn genetic stains.
Based on your specific condition, your dentist will create a tailored treatment plan that may combine different techniques, from internal bleaching to veneers, to achieve the best possible outcome. Since dental bonding can effectively mask genetic discoloration, it’s often included as part of a comprehensive treatment approach.
Professional Vs Home Options
The decision between professional and at-home teeth whitening treatments involves comparing several essential factors: effectiveness, speed, cost, and safety.
When evaluating these whitening techniques, you’ll find significant treatment comparisons between the two options. Professional methods deliver maximum brightness more effectively than any DIY solution.
- Professional treatments use 25-40% hydrogen peroxide concentration, delivering up to 8 shades lighter in a single session, while at-home kits contain only 3-10% peroxide for gradual results.
- You’ll achieve immediate results in 1-2 hours with professional whitening, compared to several weeks with home treatments.
- Professional options cost $350-$1200 but last longer, while home kits range from $5-$600 with more frequent touch-ups needed.
- Dental supervision guarantees safety and ideal results for professional treatments, whereas home kits require careful adherence to instructions to avoid complications. Protective measures like gum shields and barriers are used during professional treatments to prevent soft tissue irritation.
Safety First, Results Later
Selecting the safest whitening treatment must take precedence over achieving rapid results, especially for those with genetic tooth discoloration.
For ideal tooth safety, you’ll want to begin with a professional screening to check for contraindications like dry mouth, exposed roots, or enamel erosion that could increase whitening risks.
Choose products with the ADA Seal of Acceptance and lower peroxide concentrations, particularly carbamide peroxide-based options that cause less sensitivity. The whitening process works as oxygen molecules penetrate the tooth structure to break down stains.
You’ll achieve better results using custom-fitted trays under professional supervision rather than aggressive in-office treatments. It’s crucial to wait until children are at least 14 years old before considering any whitening procedures.
Monitor your patients for side effects and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Remember to advise them about temporary sensitivity and gum irritation while emphasizing the importance of good oral hygiene and avoiding acidic foods during treatment.
Treatment Plans by Condition
Determining the most effective treatment approach for genetic tooth discoloration requires careful evaluation of each patient’s specific condition.
Your dentist will assess your stain types and recommend appropriate treatment options based on severity and dental health.
Here’s what you can expect for different conditions:
- Mild extrinsic stains: Professional whitening treatments using hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, typically requiring 30-60 minute sessions.
- Moderate intrinsic stains: Dental bonding with composite resin, offering a cost-effective single-visit solution.
- Severe genetic discoloration: Porcelain veneers for lasting results, especially when whitening proves ineffective.
- Structural concerns: Full crowns or alternative restorative treatments when teeth need both cosmetic improvement and structural reinforcement.
Your treatment plan may combine multiple approaches to achieve the best results while preserving your dental health.
Preventive Care and Maintenance Strategies

Managing genetic tooth discoloration requires a thorough preventive care strategy that combines daily oral hygiene, professional dental care, and lifestyle modifications.
To maintain ideal results, you’ll need to implement consistent preventive techniques and follow recommended maintenance schedules.
Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and floss regularly to remove plaque buildup.
Schedule professional cleanings every six months for early detection and treatment of discoloration.
Use protective dental products like whitening toothpaste and mouth rinses to defend against staining.
You can further protect your teeth by limiting exposure to staining foods and beverages, maintaining a balanced diet rich in enamel-strengthening nutrients, and quitting smoking.
For enhanced protection, consider dental sealants or custom night guards, especially if you’re genetically predisposed to tooth discoloration.
Managing Sensitivity During Treatment
You’ll need to incorporate desensitizing products before and during your whitening treatment, including specialized toothpastes, gels, and varnishes containing potassium nitrate or fluoride.
To minimize discomfort, it’s crucial to start with lower concentrations of whitening agents and gradually increase exposure time as your teeth adjust.
If you’re genetically predisposed to sensitivity, you’ll benefit from spacing out your whitening sessions and using custom-fitted trays that provide controlled application of the bleaching agent.
Desensitizing Products and Methods
While pursuing a whiter smile through genetic tooth discoloration treatment, you’ll likely encounter some tooth sensitivity.
Using desensitizing gels and protective products can greatly reduce discomfort while maintaining treatment effectiveness. These proven solutions help protect your enamel and minimize sensitivity.
- Apply specialized desensitizing gels like UltraEZ in custom trays before or after whitening sessions for quick relief.
- Use toothpaste containing potassium nitrate or arginine-calcium carbonate consistently throughout your whitening journey.
- Consider whitening systems with built-in desensitizers, such as Kör, which offers simultaneous bleaching and comfort.
- Maintain enamel protection by using desensitizing products before, during, and after treatments to create a protective barrier.
These methods work by blocking dentinal tubules and reducing nerve sensitivity, allowing you to continue your whitening treatment comfortably.
Gradual Treatment Approach
A gradual approach to tooth whitening considerably reduces sensitivity risks while achieving lasting results. Start with lower concentrations of whitening agents and shorter application times, then make gradual adjustments as your teeth build tolerance.
Your dentist can create personalized schedules based on your specific sensitivity levels and genetic predisposition.
During treatment, avoid hot, cold, or acidic foods immediately after whitening sessions. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush with lukewarm water to prevent additional sensitivity.
If you experience discomfort, consider temporary alternatives like gentle polishing or fluoride treatments between sessions. Regular dental check-ups allow your provider to monitor progress and modify your treatment plan accordingly.
This measured approach helps protect your enamel while still delivering the whitening results you’re seeking.
Alternative Cosmetic Solutions

Since genetic tooth discoloration doesn’t always respond to conventional whitening methods, several alternative cosmetic solutions can effectively mask or correct stubborn stains.
Your dentist can recommend appropriate veneer options or bonding techniques based on your specific condition and goals.
Here are your main cosmetic treatment options:
- Porcelain veneers – provide lasting results and dramatic improvements for severe staining, though they require some enamel removal.
- Dental bonding – offers a quick, minimally invasive solution for minor discoloration at a lower cost.
- Ceramic crowns – ideal when you need both cosmetic improvement and structural reinforcement.
- Combination treatments – may include initial whitening followed by targeted restorative work for best results.
Your dentist will evaluate your tooth structure and stain severity to determine the most effective approach for your situation.
Diet and Lifestyle Adjustments
Making strategic diet and lifestyle adjustments can greatly impact the appearance of genetically discolored teeth, even when traditional whitening methods fall short.
Focus on incorporating nutrient sources like calcium-rich dairy products and phosphorus-dense lean proteins to strengthen your enamel and protect against further discoloration.
Optimize your hydration habits by drinking plenty of water throughout the day to maintain healthy saliva flow.
When consuming staining beverages like coffee or red wine, use a straw to minimize contact with your teeth, and rinse immediately afterward.
Choose fiber-rich fruits and vegetables to naturally clean your teeth, but limit acidic foods that can weaken enamel.
Additionally, eliminate tobacco use and manage stress levels, as these factors can profoundly affect tooth appearance and overall oral health.
Long-Term Treatment Planning
Developing a thorough long-term treatment plan is essential for managing genetic tooth discoloration effectively. Your dentist will work with you to create a customized strategy that addresses your specific needs while ensuring ongoing monitoring of your oral health.
- Start with professional whitening treatments, which you’ll need to repeat every 5-7 years to maintain results, especially with genetic conditions.
- Schedule regular dental cleanings every six months to remove surface stains and assess your tooth condition.
- Consider combining treatments like internal bleaching, bonding, or veneers based on the severity of your discoloration.
- Commit to long-term care through frequent check-ups, allowing your dentist to adjust treatments as your enamel and tooth condition change over time.
Realistic Expectations and Results
Understanding your genetic tooth composition plays an essential role in setting realistic whitening expectations. Your natural tooth color stems from a combination of enamel thickness and dentin shade, both influenced by genetic variability. These factors determine how well your teeth will respond to whitening treatments.
You’ll need to recognize that whitening primarily affects surface stains while leaving your underlying genetic tooth composition unchanged. If you have naturally darker dentin or thinner enamel, you may achieve more modest results compared to someone with thicker enamel.
Treatment outcomes can vary considerably based on your unique genetic makeup, and maintaining results requires consistent care. While professional whitening can improve most smiles, it’s important to work with your dentist to establish achievable goals based on your specific genetic factors.
Customized Home Care Routines
To effectively manage genetic tooth discoloration at home, you’ll need a carefully tailored care routine that combines proper product selection with consistent application methods.
Your personalized routines should focus on both prevention and improvement while protecting your enamel’s integrity.
- Choose gentle whitening products specifically designed for at-home use, avoiding harsh abrasives that could damage genetically altered enamel.
- Follow a twice-daily oral hygiene regimen with specialized toothpaste and antimicrobial treatments like oil pulling.
- Monitor your progress through regular photos and dental checkups every 4-6 weeks to adjust your home care strategy.
- Maintain a stain-prevention lifestyle by limiting colored beverages, rinsing after meals, and increasing consumption of naturally cleansing foods like apples and carrots.
Remember to adjust your routine based on sensitivity levels and professional guidance for best results.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Genetic Tooth Discoloration Skip Generations in Families?
While 25% of hereditary traits can skip generations, you’ll find genetic tooth discoloration often bypasses family members, especially in recessive and X-linked patterns where carriers don’t show symptoms.
What Age Do Genetic Tooth Conditions Typically First Become Visible?
You’ll notice early signs of genetic tooth conditions when teeth first emerge, typically around 6 months for baby teeth. These hereditary factors affect both primary and permanent teeth throughout childhood.
Are There Specific Genetic Tests Available for Tooth Discoloration Conditions?
You can get genetic testing for *DSPP* mutations causing dentinogenesis imperfecta and targeted gene panels for amelogenesis imperfecta. Both tests help diagnose specific discoloration conditions affecting your teeth.
How Do Pregnancy Hormones Affect Genetic Tooth Discoloration Treatments?
Like a ship in stormy seas, pregnancy hormonal changes can intensify your genetic tooth discoloration by increasing gum sensitivity and enamel vulnerability. You’ll want to postpone treatments until after delivery.
Can Orthodontic Treatment Improve Genetic Tooth Discoloration Outcomes?
You’ll see limited direct improvement, but orthodontic benefits include better teeth alignment, allowing more uniform whitening agent application. This indirect effect can enhance your overall aesthetic improvements post-treatment.
References
- https://www.i20familydental.com/blog/2023/10/13/all-about-teeth-whitening-and-genetics/
- https://www.airportroaddental.com/tooth-discoloration-causes-types-and-treatment
- https://www.salinasdental.com/blog/can-discolored-and-stained-teeth-be-hereditary/
- https://www.perfectsmiles.net/2024/06/17/genetics-and-discolored-teeth/
- https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/tooth-discoloration
- https://www.fsdentalarts.com/blog/?p=49
- https://www.deandentalcare.com/blog/2021/08/12/stained-teeth-genetics/
- https://www.budadental.com/blog/stained-teeth-and-the-role-of-genetics/
- https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/dentinogenesis-imperfecta/
- https://www.gatewayfamilydentist.com/can-genetics-cause-tooth-discoloration