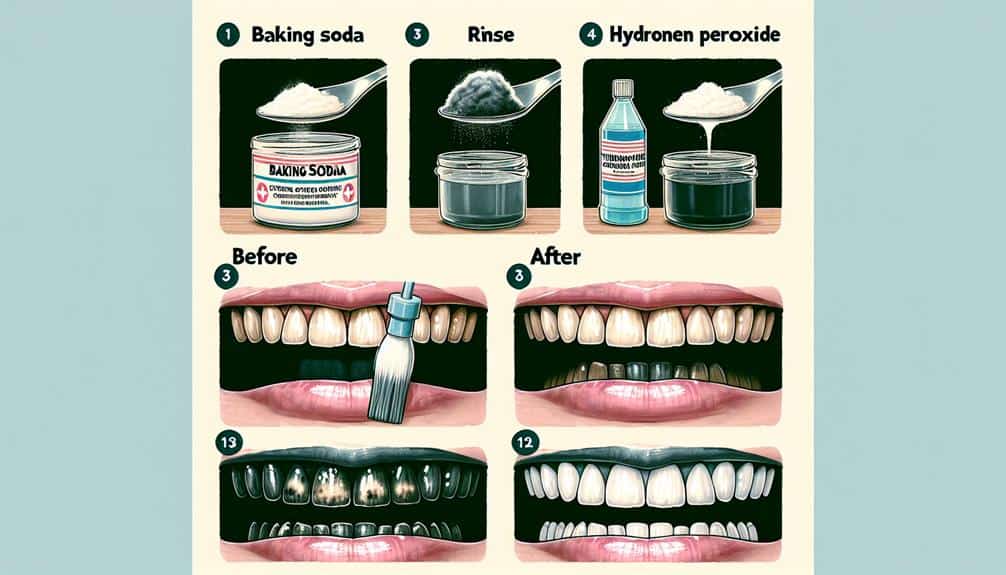
Tetracycline stains cling to enamel's essential calcium-rich hydroxyapatite structure, making removal challenging. The severity of the stain dictates its depth penetration, potentially reaching the dentin layer. Deeper stains seep into porous enamel more stubbornly, requiring advanced removal methods. Traditional whitening techniques struggle to combat these intrinsic tetracycline stains due to their resistance to conventional agents. However, advancements like stain-resistant materials, laser therapy, and photochemical activation offer enduring solutions. Implementing long-term oral hygiene practices is vital for managing these challenging stains. Understanding these complexities sets the stage for effectively addressing tetracycline stains on teeth.
Key Points
- Tetracycline stains bind with enamel's calcium ions.
- Deeper stains penetrate into the dentin layer.
- Porous enamel allows for deeper stain seepage.
- Traditional whitening methods struggle with intrinsic stains.
- Tetracycline molecules resist conventional whitening agents.
Tetracycline Stains and Tooth Structure
When dealing with tetracycline stains on teeth, understanding the interaction between these stains and the tooth structure is essential for effective removal. Enamel composition plays a vital role in how tetracycline stains manifest.
Enamel, the outer layer of the tooth, is primarily composed of hydroxyapatite crystals. These crystals form a dense structure that provides strength and protection to the tooth. However, tetracycline stains can penetrate this enamel due to their ability to bind with calcium ions in hydroxyapatite, leading to discoloration.
Stain severity also influences the interaction between tetracycline stains and tooth structure. The depth to which the stains penetrate the enamel affects the difficulty of removal. Deeper stains may reach the dentin layer beneath the enamel, making it more challenging to eliminate the discoloration effectively.
Understanding the composition of enamel and the severity of tetracycline stains is crucial in developing targeted strategies for removing these stubborn discolorations from teeth.
Factors Affecting Stain Penetration
Factors influencing the penetration of stains on teeth include the composition of enamel and the depth of the discoloration. Stain depth plays a pivotal role in how difficult it's to remove discoloration. Deeper stains penetrate further into the porous enamel, making them more challenging to eliminate. Enamel composition also affects stain penetration; porous enamel allows stains to seep in more deeply compared to less porous enamel.
The depth of the stain is a significant factor in determining the success of whitening treatments. Deeper stains require more aggressive methods to reach and lighten them effectively. Porous enamel, which is more common in individuals with certain genetic factors, can make it harder to remove stains as they tend to penetrate deeper into the tooth structure.
Understanding these factors is essential when considering how to address tetracycline stains on teeth. Tailoring treatment approaches based on the specific nature of the stain can lead to more successful outcomes in addressing challenging discolorations.
Challenges in Traditional Whitening Methods
Traditional whitening methods commonly face challenges in effectively removing deep-seated stains on teeth. While these methods can be successful in treating surface stains caused by food and beverages, they often fall short when dealing with intrinsic stains like tetracycline discoloration. Limitations of traditional whitening treatments include their inability to penetrate the enamel deeply enough to target the underlying pigments responsible for tetracycline stains. The structure of tetracycline molecules makes them particularly difficult to break down with conventional whitening agents, leading to suboptimal results.
In light of these challenges, individuals seeking to address tetracycline stains may consider alternative approaches to achieve more satisfactory outcomes. Options such as microabrasion, veneers, and bonding offer potential solutions by covering or removing the stained enamel rather than attempting to bleach it. These alternatives can provide more noticeable and long-lasting improvements for individuals struggling with tetracycline discoloration, circumventing the limitations of traditional whitening methods.
Advanced Treatments for Tetracycline Stains
Exploring innovative treatments for tetracycline stains reveals promising advancements in effectively addressing deep-seated discoloration on teeth. Stain resistant materials have emerged as a cutting-edge solution in combating the stubborn nature of tetracycline stains. These materials, often used in dental restorations, not only provide a durable and natural-looking solution but also offer resistance to future staining, making them a valuable option for individuals with tetracycline discoloration.
Furthermore, emerging technologies like laser therapy and photochemical activation of whitening agents show great potential in targeting tetracycline stains at a deeper level. Laser treatments can penetrate the enamel and break down the accumulated pigmentation, leading to significant improvements in the appearance of stained teeth. Photochemical activation, on the other hand, enhances the effectiveness of whitening agents, ensuring better outcomes for individuals struggling with tetracycline stains.
These advanced treatments represent a shift towards more targeted and efficient approaches in managing tetracycline stains, offering hope to individuals seeking lasting solutions for their dental discoloration.
Long-Term Strategies for Stain Management
Implementing a thorough oral hygiene routine is key to effectively managing long-term stain accumulation on teeth. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily can help prevent stains from settling in. Additionally, consider incorporating dietary modifications by reducing the consumption of foods and beverages that are known to cause staining, such as coffee, tea, and red wine. Drinking water after consuming staining substances can also help wash away pigments before they adhere to the teeth.
Regular professional cleanings are essential for long-term stain management. Dentists can use specialized tools to remove stubborn stains that may not be eliminated through regular brushing. Professional cleanings also help prevent tartar buildup, which can exacerbate the appearance of stains on teeth over time. During these cleanings, your dentist can provide personalized recommendations for at-home care to maintain a brighter, stain-free smile. By combining diligent oral hygiene practices with professional dental cleanings, you can effectively manage and prevent long-term stain accumulation on your teeth.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Common Are Tetracycline Stains on Teeth in the General Population?
Tetracycline stains on teeth are rare, affecting only about 3% of the general population. Treatment options include professional whitening and veneers. Preventive measures involve avoiding tetracycline during pregnancy and in children under 8 years old.
Are There Any Home Remedies or Over-The-Counter Products That Can Effectively Remove Tetracycline Stains?
To remove tetracycline stains, consider natural remedies like baking soda or over-the-counter products such as whitening toothpaste. While natural options are safe but may lack effectiveness, OTC products offer better results. Consult a dentist for professional advice.
Can Tetracycline Stains on Teeth Cause Any Long-Term Health Issues?
Long-term consequences of tetracycline stains on teeth can include aesthetic concerns and potential impact on oral health. Treatment options vary but prevention through dental care is essential. Regular check-ups can help monitor and address any issues.
Are There Any Specific Dietary or Lifestyle Factors That Can Worsen Tetracycline Stains on Teeth?
To worsen tetracycline stains on teeth, consider dietary habits and lifestyle choices. Avoid dark beverages, tobacco, and acidic foods. Prioritize oral hygiene and regular dental care. These factors can impact the severity and persistence of tetracycline stains.
Is It Possible to Prevent Tetracycline Stains on Teeth From Developing in the First Place?
To prevent tetracycline stains on teeth, focus on preventative measures like avoiding tetracycline antibiotics during tooth development. Treatment options for existing stains include professional whitening, bonding, or veneers. Consulting a dentist is essential for personalized advice.