For genetic tooth discoloration, you’ll need a multi-faceted approach combining professional treatments with consistent at-home care. Consider porcelain veneers for permanent correction of deep staining, or opt for professional whitening treatments for milder cases. You’ll want to maintain rigorous oral hygiene using non-abrasive techniques, fluoride-rich products, and remineralizing agents. Understanding your specific genetic factors will help determine the most effective brightening strategy for your unique case.
Key Takeaways
- Professional porcelain veneers provide a permanent solution for severe genetic discoloration by masking deep stains while maintaining natural appearance.
- Custom-fitted whitening trays with professional-grade gels offer effective at-home treatment for mild to moderate genetic staining.
- Regular professional cleanings combined with fluoride treatments help maintain tooth brightness and strengthen enamel against discoloration.
- Dental bonding effectively addresses localized genetic staining and can be customized to match surrounding tooth color.
- Comprehensive treatment plans incorporating genetic testing can target specific mutations and combine multiple approaches for optimal results.
Understanding Genetic Factors in Tooth Color
While your natural tooth color is largely determined by genetics, understanding these inherited factors can help you make informed decisions about cosmetic dental treatments.
Your genetic inheritance affects both your enamel thickness and the color of the underlying dentin layer, which appears naturally yellowish. When you have thinner enamel, more of this yellow dentin shows through. Research shows that ancestral genetic heritage plays a significant role in determining your dentin’s natural hue and brightness.
Genetics determine both enamel thickness and dentin color, affecting your natural tooth appearance. Thinner enamel reveals more of the yellow dentin underneath.
Your genes also control how dense and translucent your enamel is, impacting how light reflects off your teeth. If you’ve inherited thicker enamel, your teeth typically appear whiter. Some people inherit conditions like dentinogenesis imperfecta, which causes teeth to appear grayish and transparent.
Additionally, your genetic makeup influences how susceptible your teeth are to staining from foods and beverages. Understanding these inherited characteristics can help your dental professional develop the most effective treatment approach for achieving your desired smile aesthetics.
Professional Treatment Options for Inherited Discoloration
Since genetic tooth discoloration often requires more intensive intervention than surface staining, dental professionals offer several specialized treatment options to address inherited color variations.
For severe inherited tooth stains, porcelain veneers provide a long-lasting solution, effectively masking deep discoloration while improving overall tooth appearance. Regular dental check-ups are essential to monitor the condition of treatments and ensure optimal results.
If your genetic discoloration causes are less severe, professional teeth whitening using high-concentration peroxide can yield noticeable improvements, particularly when combined with regular dental cleanings.
Dental bonding offers a middle-ground approach for localized genetic staining, while full crowns may be necessary if structural concerns accompany the discoloration. Those with Dentinogenesis Imperfecta may especially benefit from crowns due to their weak, brittle teeth.
You’ll find that most treatments require periodic maintenance or replacement, but they effectively transform genetically discolored teeth into a brighter, more confident smile.
At-Home Care Strategies for Genetically Yellow Teeth
Managing genetically yellow teeth at home requires a targeted approach that complements professional treatments. You’ll need to take into account your specific genetic influences, particularly your enamel characteristics, when selecting brightening methods. For those with dentinogenesis imperfecta, special care must be taken as aggressive whitening can further damage compromised dentin.
Start with gentle, non-abrasive cleaning techniques using fluoride toothpaste twice daily and regular flossing to prevent additional staining. If you have inherited enamel fragility, opt for remineralizing products containing calcium phosphates rather than harsh whitening agents. Thicker enamel tends to respond better to whitening treatments, so those with naturally thin enamel should be more cautious.
Monitor your enamel’s response to any brightening attempts, and adjust your routine accordingly. Protect your genetic tooth composition by limiting staining beverages, maintaining proper hydration, and using an electric toothbrush for controlled pressure.
Remember that over-the-counter whitening products may have limited effectiveness on genetically yellow dentin, so focus on preserving enamel health while managing expectations.
Dental Veneer Solutions for Permanent Color Correction
For patients seeking a permanent solution to genetic tooth discoloration, dental veneers offer a transformative option that combines aesthetic excellence with long-term stability.
These custom-fabricated porcelain shells provide immediate color correction while preserving natural tooth structure. High-quality veneers can maintain their bright appearance for 10 to 15 years. The process begins with an initial consultation to determine the most suitable veneer solution for each patient.
- Porcelain veneers deliver superior stain resistance and color stability compared to natural enamel
- Custom shade matching guarantees seamless integration with surrounding teeth
- Advanced layering techniques using opaque composites effectively mask severe discoloration
- Minimal tooth preparation maintains structural integrity while achieving desired aesthetics
- Veneers longevity typically exceeds traditional whitening methods with proper care
When considering aesthetic considerations, you’ll find veneers particularly beneficial for treating intrinsic discoloration resistant to conventional whitening.
This solution offers predictable, lasting results while addressing multiple cosmetic concerns simultaneously, making it an ideal choice for extensive smile enhancement.
Protective Measures for Fragile Genetic Enamel
Beyond aesthetic corrections, patients with genetically fragile enamel require extensive protective strategies to maintain long-term oral health.
You’ll need to implement thorough enamel remineralization strategies, including specialized toothpaste containing calcium, phosphate, and fluoride compounds. Professional fluoride treatments and dental sealants provide essential protection against further deterioration. Children with tooth discoloration may show rough surface texture, indicating potential enamel hypoplasia development.
Dietary enamel protection plays an important role in preserving compromised tooth structure. You should limit acidic foods and beverages while increasing consumption of calcium-rich nutrients. Consulting with an orthodontic professional immediately is recommended when symptoms of enamel thinning appear.
Regular dental visits every six months allow for monitoring of enamel integrity and timely intervention. For mechanical protection, nightguards can prevent damage from grinding, while gentle brushing techniques with soft-bristled brushes help maintain delicate enamel.
Remember to address underlying conditions like dry mouth or acid reflux that could accelerate enamel wear.
Lifestyle Adjustments to Minimize Further Staining
While living with genetic tooth discoloration presents ongoing challenges, you’ll need to implement extensive lifestyle modifications to prevent further staining.
Focus on diet modifications and hydration habits that protect your teeth’s appearance while supporting overall oral health.
- Consume crunchy fruits and vegetables to naturally clean teeth surfaces and stimulate protective saliva production.
- Switch to drinking staining beverages through straws, and rinse immediately with water afterward.
- Maintain ideal hydration by drinking water throughout the day, especially after meals.
- Add calcium-rich dairy products to strengthen enamel resistance against discoloration.
- Eliminate tobacco use and minimize dark alcoholic beverages that intensify staining.
These targeted adjustments will help preserve your smile’s aesthetics while managing genetic enamel vulnerability.
Regular implementation of these practices supports long-term discoloration management.
Modern Whitening Technologies for Hereditary Cases
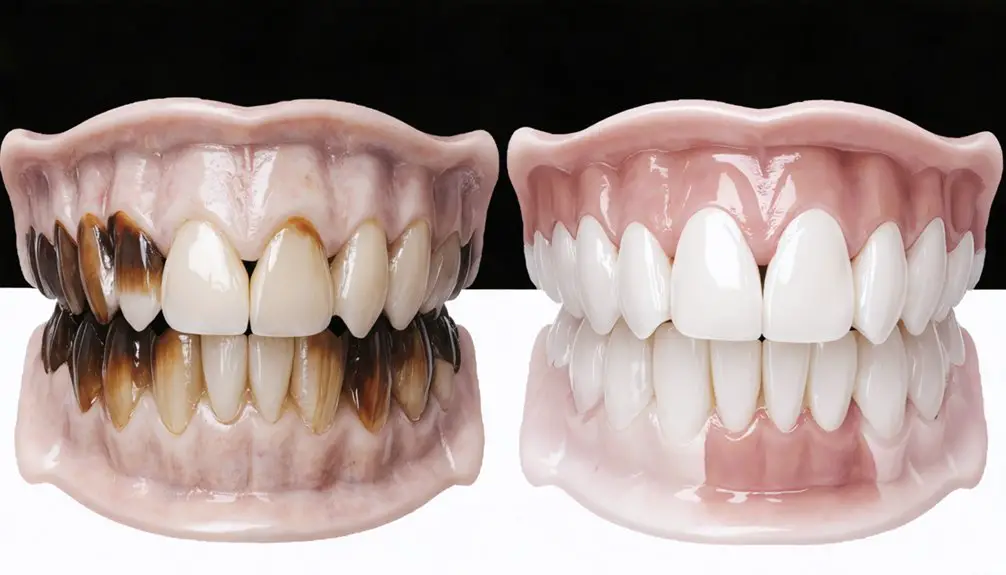
Modern whitening technologies have revolutionized treatment approaches for hereditary tooth discoloration, offering multiple specialized solutions for even the most challenging genetic cases.
You’ll find professional in-office treatments using high-concentration peroxides can brighten teeth up to eight shades, though genetic discoloration often requires additional interventions.
For deeper intrinsic stains, you’ve got options like custom-fitted trays with concentrated gels for at-home use, or more permanent solutions like porcelain veneers and crowns.
While whitening limitations exist due to genetic factors affecting enamel composition, internal bleaching and microabrasion techniques can target specific areas of discoloration.
Your success depends on carefully planned treatment combinations that consider your unique genetic profile, ensuring the most effective approach to achieving your desired aesthetic results.
Long-Term Management of Genetic Dental Conditions
To manage genetic tooth discoloration effectively long-term, you’ll need to maintain rigorous preventive care practices, including enhanced oral hygiene routines, frequent professional cleanings, and protective treatments like fluoride applications.
Your dentist will closely monitor treatment progress through regular examinations, diagnostic imaging, and detailed documentation of changes in tooth color and structure over time.
Professional support involves ongoing adjustments to your personalized treatment plan, incorporating specialists when needed and updating interventions based on your genetic profile and response to treatments.
Preventive Care Best Practices
Maintaining ideal dental health with genetic tooth discoloration requires five essential preventive care strategies: consistent oral hygiene, dietary modifications, regular professional care, protective treatments, and behavioral adaptations.
To optimize your preventive strategies and dental hygiene routine:
- Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and use whitening formulas several times weekly to combat stain accumulation.
- Follow a calcium-rich diet while limiting staining beverages, using straws when consuming pigmented drinks.
- Schedule biannual dental checkups for professional cleanings and early intervention.
- Utilize protective treatments like fluoride applications and sealants to strengthen genetically compromised enamel.
- Implement gentle brushing techniques and wear mouthguards during sports to prevent trauma that could worsen existing discoloration.
Monitoring Treatment Progress
Successful management of genetic tooth discoloration depends on systematic monitoring and documentation of treatment progress over time.
You’ll need regular dental follow-ups to evaluate treatment effectiveness and durability, whether you’ve opted for dental bonding, veneers, or whitening procedures. Your dentist will track enamel integrity and document changes through clinical photographs and detailed patient records.
Treatment timelines vary based on the specific intervention – dental bonding typically needs touch-ups every 5-7 years, while veneers may last 5-15 years.
Progress documentation helps your dental team adjust treatment strategies and schedule maintenance procedures accordingly. Your personalized monitoring plan will incorporate genetic markers and biomarkers when available, enabling more precise tracking of treatment outcomes and allowing for timely adjustments to your care protocol.
Professional Support and Adjustments
Long-term management of genetic tooth discoloration requires consistent professional oversight and a collaborative approach between specialists.
You’ll need regular evaluations to monitor your treatment’s effectiveness and make necessary adjustments, particularly when dealing with enamel fragility issues. Your care team may include cosmetic dentists, genetic counseling specialists, and restorative experts working together to optimize your results.
- Schedule check-ups every 6 months to assess restoration durability
- Monitor sensitivity levels and adjust treatments accordingly
- Track changes in tooth color and structural integrity
- Receive ongoing guidance for dietary and lifestyle modifications
- Participate in periodic maintenance sessions to sustain results
Your dental team will adapt your treatment plan based on how your teeth respond, ensuring the most effective long-term management of your genetic condition while preserving your smile’s health and appearance.
Combining Treatments for Optimal Results
While genetic tooth discoloration presents unique challenges, combining multiple treatment approaches often yields superior aesthetic outcomes compared to single interventions.
You’ll achieve ideal treatment synergy by starting with microabrasion or mechanical cleaning before proceeding to professional whitening. For severe cases, you can pair in-office bleaching with custom porcelain veneers or dental bonding to address widespread discoloration.
If you’re dealing with root canal-treated teeth, internal whitening combined with restorative coverage offers thorough improvement.
Your treatment plan should incorporate genetic testing results to target specific mutations effectively. This personalized approach helps determine whether you’ll need periodic touch-ups or more permanent solutions like crowns.
Preventive Care for Future Generations

If you’re concerned about genetic tooth discoloration in your family, early genetic testing can identify specific inherited conditions that affect tooth color and structure before visible symptoms appear.
You’ll benefit from creating a detailed family dental plan that incorporates preventive treatments, lifestyle modifications, and regular professional monitoring based on your genetic predisposition.
Your children’s dental care should include protective measures like fluoride treatments, sealants, and specialized cleaning protocols tailored to their genetic risk factors for maintaining ideal tooth appearance and health.
Early Genetic Testing Benefits
Modern genetic testing has revolutionized preventive dental care by enabling early detection of hereditary tooth discoloration disorders. Through genetic screening, you’ll discover your predisposition to enamel defects and other dental conditions before visible symptoms emerge.
This knowledge empowers you to take proactive steps in protecting your oral health.
- Identifies risk for conditions like amelogenesis imperfecta and dentinogenesis imperfecta
- Enables customized prevention plans targeting specific genetic vulnerabilities
- Guides ideal timing and frequency of professional cleanings
- Determines most effective fluoride treatment protocols
- Supports early specialist referral for advanced gene-based therapies
Family Dental Planning Strategies
Because genetic tooth discoloration can greatly impact future generations, thorough family dental planning has become essential for preserving oral health across lineages.
You’ll want to start by collecting detailed family dental histories to identify inherited risks and recurring conditions that affect tooth color. This data enables creation of targeted prevention strategies based on your family genetics.
Implement coordinated dental care schedules for all family members, focusing on regular professional cleanings and early intervention.
You should customize preventive protocols, including specialized fluoride treatments and protective sealants, based on your family’s specific enamel vulnerabilities.
Additionally, establish nutrition guidelines that minimize staining foods and beverages while promoting enamel-strengthening choices.
Consider genetic counseling to better understand your family’s risk factors and develop appropriate long-term maintenance strategies.
Protective Pediatric Dental Care
While genetic tooth discoloration poses long-term challenges, implementing protective pediatric dental care early can greatly minimize its impact on future generations.
You’ll need to guarantee consistent dental access through regular preventive visits and establish proper oral care routines from infancy.
To maximize your child’s dental health outcomes:
- Schedule at least 7 preventive sessions annually, particularly during critical tooth development phases
- Apply fluoride varnishes and sealants as recommended by your pediatric dentist
- Monitor and limit sugar consumption across all developmental stages
- Maintain daily brushing routines with direct parental supervision
- Partner with community dental programs to supplement care when needed
These protective measures become especially essential for children with genetic predispositions to tooth discoloration, as early intervention through pediatric preventive care greatly reduces future complications and treatment needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Genetic Tooth Discoloration Skip Generations in Families?
In 75% of cases, hereditary factors can make tooth discoloration skip generations through recessive genes or X-linked patterns. You’ll notice these familial patterns when carriers pass mutations without showing symptoms.
Are Children With Genetic Tooth Discoloration More Prone to Dental Anxiety?
You’ll find that children with genetic tooth discoloration often experience higher dental anxiety due to both inherited genetic factors and psychological responses to visible dental differences, affecting their comfort during treatment visits.
Do Genetic Tooth Problems Affect Speech Development in Young Patients?
Like a piano missing keys affects music, genetic tooth problems can impact your child’s speech clarity. You’ll need targeted dental interventions and speech therapy to support proper sound development.
How Does Pregnancy Impact Existing Genetic Tooth Discoloration Conditions?
Your existing genetic tooth discoloration may worsen during pregnancy due to hormonal changes affecting enamel sensitivity and plaque retention. You’ll need enhanced dental care to manage increased susceptibility to staining and pigmentation.
Can Genetic Tooth Discoloration Worsen With Certain Vitamin Deficiencies?
Like dominoes falling, your genetic tooth discoloration can intensify when vitamin deficiencies disrupt vitamin absorption. Particularly, low vitamin D and A levels compromise your enamel health, worsening existing genetic staining patterns.
References
- https://www.airportroaddental.com/tooth-discoloration-causes-types-and-treatment
- https://www.salinasdental.com/blog/can-discolored-and-stained-teeth-be-hereditary/
- https://www.perfectsmiles.net/2024/06/17/genetics-and-discolored-teeth/
- https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/tooth-discoloration
- https://citydentalnyc.com/tooth-discoloration-causes-treatment/
- https://onestopdentalcolorado.com/the-role-of-genetics-in-tooth-color/
- https://www.deandentalcare.com/blog/2021/08/12/stained-teeth-genetics/
- https://www.mynewportdentist.com/blog/2024/12/13/is-some-tooth-discoloration-hereditary/
- https://www.gatewayfamilydentist.com/can-genetics-cause-tooth-discoloration
- https://www.docronan.com/blog/2023/03/04/can-tooth-discoloration-be-genetic/